Pepper plant diseases and pests are very common. Pepper is the pillars of world cuisine due to their intense colors and wide range of tastes. On the other hand, growing these food staples does have its own challenges namely pests and diseases that can affect yield significantly. So, for farmers and gardeners the knowledge of pest and diseases of pepper is necessary to ensure appropriate management strategies that guarantee successful pepper production. This comprehensive guide covers the most common pepper plant diseases and pests, providing in-depth information on their identification, symptoms, and management practices that are sustainable.

Management: Early detection and intervention is the key to controlling aphids. Ladybugs, lacewings and hoverflies are natural predators that can be encouraged using biological control methods. For more extensive infestations, organic treatments like insecticidal soaps or neem oil can be used. Aphids can also be repelled from plants by reflective mulches.
Solution: To combat aphid infestations on peppers, consider using natural fungal biocontrol agents like Metarhizium anisopliae, or Beaveria WP. These eco-friendly solutions effectively reduce aphid populations without relying on chemical pesticides.

Management: However, the best way to manage pepper weevils is through pheromone traps that monitor and control adult populations. Infested fruits must be regularly inspected and removed. Weevil populations can also be controlled by keeping the field borders clean and using organic pesticides such as Beauveria bassiana.
Solution: For controlling pepper plant diseases and pests, Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae offer effective, eco-friendly solutions. These organic biopesticides target weevil populations, promoting sustainable pest management.

Management: Spider mite management involves increasing humidity and using overhead watering to break their activity. A biological control technique that can be used is the introduction of predatory mites such as Phytoseiulus persimilis. Some of the organic control methods are horticultural oils and insecticidal soaps.
Solution: To combat spider mites, employing organic solutions like Beaveria WP is highly effective. These natural fungal agents specifically target mite populations, providing an environmentally friendly and sustainable approach to pest management.

Solution: Apply insecticides like BT Thuricide when beet armyworm are in their nymphal stage.

Solution: Apply insecticides like BT Thuricide or bacillus thuringiensis or Metarhizium anisopliae.

Solution: To address beetles that damage plant leaves, Myco Pestop and Metarhizium anisopliae offer effective control. These natural agents target and manage beetle populations while maintaining plant health.

Solution: To combat small flies and their larvae that tunnel through leaves, apply BT Thuricide. This targeted insecticide effectively controls infestations while preserving the health of your plants.

Solution: For leaf-rolling moth larvae, apply BT Thuricide. This insecticide effectively targets the larvae within their shelters, protecting your plants from further damage.

Solution: To address issues with small, slender insects causing stippling on leaves and flower disfigurement, apply biocontrol agents like Beaveria WP or Metarhizium anisopliae. These solutions effectively control the pests while being environmentally friendly.

Solution: To tackle fruit-boring caterpillars, apply Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis. This specific strain effectively targets the larvae, preventing fruit damage and subsequent rot.

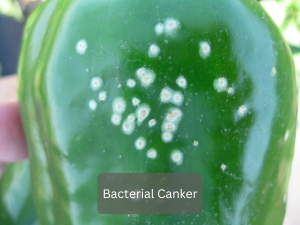
Features and symptoms: pepper plant diseases identification can be done under warm, wet conditions. The symptoms include dark, watery spots on leaves and fruits that are usually surrounded by a yellow halo. Severe infections cause leaf fall and low yields.
Management: Management of bacterial spot requires the use of disease-resistant pepper varieties and application of copper fungicides, particularly after rainfall or overhead irrigation. Rotating crops and avoidance of working in wet fields will help to prevent the spread of this disease.
Solution: To manage pepper plant diseases and pests, apply biocontrol agents like Bactonus, or Bacillus Polymyxa. These beneficial bacteria offer a natural solution to combat the disease and promote healthy plant growth.

Features and symptoms: Powdery mildew is a fungal infection that produces white powder on the leaf’s surface. It impacts the plant’s photosynthetic capacity and vitality. The symptoms are white, powdery patches on the upper surface of leaves that can spread to cover the entire leaf. Leaves infected with the virus may turn yellow and abscise early.
Management: Manage powdery mildew by increasing air circulation around plants and lowering humidity. Sulfur-containing fungicides can be useful. Destruction of infected plant parts helps in curtailing the spread of disease.
Solution: To combat powdery mildew on plants, apply natural fungicides like Trianum V or Metilo. These treatments help in controlling the fungus while supporting the overall health of your plants.
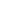
Features and symptoms: Anthracnose, caused by a fungus, primarily affects the fruits of pepper plants, especially during warm, humid conditions. It manifests as sunken, water-soaked lesions on fruits, which can enlarge and darken over time.
Management: Management strategies include avoiding overhead watering to reduce humidity, removing and destroying infected fruits, and applying organic fungicides like copper-based products or Bacillus subtilis strains. Ensuring good air circulation and practicing crop rotation are also effective.
Solution: For controlling Anthracnose in pepper plants, consider applying Trianum Shield or Trichoderma Aspellum. These organic fungicides target the fungus effectively, aiding in maintaining healthy fruit production.

Solution: To manage Cercospora Leaf Spot in plants, apply natural fungicides like Trianum V, Bacillus Velezensis, or Bacillus Amyloliquefacens. These treatments help control the disease while supporting plant health.

Solution: For seedlings affected by collapsing and root issues, apply Trianum Shield, or Trichoderma Aspellum. These biofungicides effectively prevent and treat fungal problems, promoting healthy seedling growth.

Solution: To address plant issues like yellowing foliage and wilting leaves, apply Trianum Shield, or Trichoderma Aspellum. These treatments help protect plants by enhancing their resistance to soil-borne diseases.

Solution: To combat the issue, apply Trianum V, Bacillus Velezensis, or Bacillus Amyloliquefacens. These biofungicides effectively manage the problem while promoting plant health.

Solution: Apply Trianum V to the targetted problem, aiding in restoring plant health and vigor.

Solution: Apply Cropium to enhance soil health, supporting plant vitality and preventing diseases.
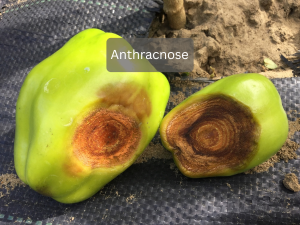
Solution: Apply biocontrol agents Bactonus, or Bacillus Polymyxa to effectively combat bacterial infections and support overall plant health.
Solution: Apply the biocontrol agents like Bactonus, or Bacillus velezensis, effectively target the problem, promoting healthier plant growth.

Solution: Applying Bactonus, Bacillus velezensis, or Bacillus Polymyxa can effectively help manage these symptoms, supporting healthier plant development.

Solution: Apply Metilo, Bacillus megaterium, or Bacillus Polymyxa to treat nutrient deficiencies, promoting healthier plant growth and getting rid of pepper plant diseases and pests.

Solution: Apply Bacillus Subtilis, Bacillus velezensis, or Bacillus Amyloliquefacens to mitigate symptoms and support healthy plant growth.

Solution: For issues such as spotted and bronzed leaves, wilting plants, and fruit with concentric rings, apply a combination of Bacillus and Trichoderma. These natural agents effectively control the symptoms and improve overall plant health.

Solution: To combat black lesions on stems, wilting plants, and circular gray-brown lesions on leaves and fruit, apply Trianum V. These biofungicides target the disease effectively, promoting healthier plant growth.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a comprehensive approach that utilizes multiple strategies to control pests and diseases. It highlights ongoing monitoring for early detection, biological control, cultural practices and the judicious use of organic pesticides. Adopting IPM, growers can protect ecological balance while ensuring sustainable pepper production.
The pepper plant diseases and pests that affect peppers must be well understood for successful pepper cultivation. The use of sustainable management practices ensures the production of healthy crops and abundant harvests. This guide can be used as a tool to fight these challenges, encouraging the adoption of sustainable and eco-friendly practices in pepper cultivation.